Hamular Notch
Ham-u-lar Notch |
Hamular Notch
Other Names: Pterygomaxillary Notch
Definition
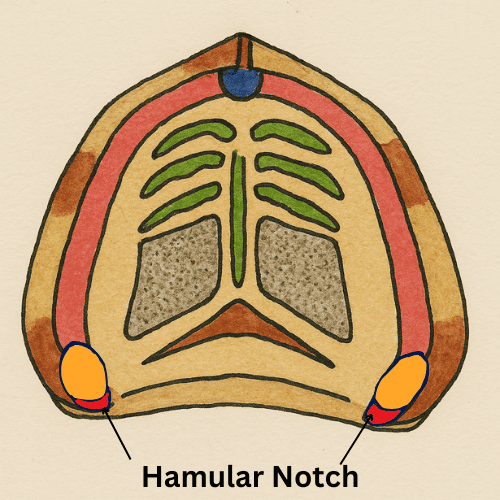
The Hamular Notch is a depression situated between the Maxillary Tuberosity & the Hamulus of Medial Pterygoid Plate. It marks the posterior limit of the maxillary arch and is a critical anatomical landmark in prosthodontics.
Description
Anatomical Landmarks
- The hamular notch lies posterior to the maxillary tuberosity.
- It extends medially and slightly downward toward the pterygoid hamulus, a hook-like projection of the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
- It’s palpable intraorally in edentulous patients and is often used as a reference point for complete denture fabrication.
How to find Hamular Notch?
- Use a mouth mirror and palpate to locate the hamular notch in edentulous patients.
- Record the area using impression compound or elastomeric materials during the border molding stage of denture construction.
- Avoid overextension into the notch area to prevent ulceration or irritation of the pterygoid hamulus.
Significance
1. Denture Fabrication:
- The hamular notch serves as a posterior landmark for determining the posterior palatal seal (PPS) in maxillary complete dentures.
- Accurate recording of the hamular notch ensures a proper seal, retention, and stability of the upper denture.
- If not captured properly, it can lead to poor suction and denture dislodgement during function.
2. Clinical Significance:
- It helps in the termination of the vibrating line, which is vital for the design of the PPS area.
- The vibrating line usually runs from one hamular notch to the other, and it’s where the soft palate begins its movement during phonation.
3. Surgical Landmark:
- In oral surgeries, particularly maxillary surgeries, the hamular notch may serve as an orientation point.
- In cases involving palatal implants, maxillary sinus surgeries, or tuberosity reduction, the hamular notch location aids in safe and precise navigation.
References
- Boucher’s Prosthodontic Treatment for Edentulous Patients.