Root Canal treatment – step by step procedure
Root Canal treatment is one of the most common treatments in dentistry done by the dentists. It is a procedure used when the infection has gone into pulp and it can’t be saved. The procedure usually takes 3 sittings when the conventional procedure is used excluding the crown placement.
Nowadays, The root can procedure can also be done in single sitting. It takes approximately 3-3.5 hours for a single sitting rct procedure.
What is a root canal?
Root Canal is the canal present in the root which is the only vital part of the tooth since it contains the pulp. The pulp is a soft tissue which is covered by enamel on the crown (coronal) portion and dentin on the root (radicular) portion.
The root canal is of different shapes in different teeth and it is also different in different person. The number of root canals also differ in every other teeth due to which a proper radiograph is needed of root canal for determining the number of root canals and their shapes.
The root canal are classified on the basis of number by different scientists out of which the most widely used are of Vertucci’s classification & Weine’s Classification.
Why root canal treatment is needed?
The Root canal procedure is used for teeth which have deceased pulp. The pain is very sharp and high when the infection involves the pulp as it is the only vital part of the tooth.
Once infected, The only option left is the removal of all the pulp inside the tooth which is known as the root canal treatment procedure. Let’s learn about the root canal treatment in the step by step guide for better understanding.
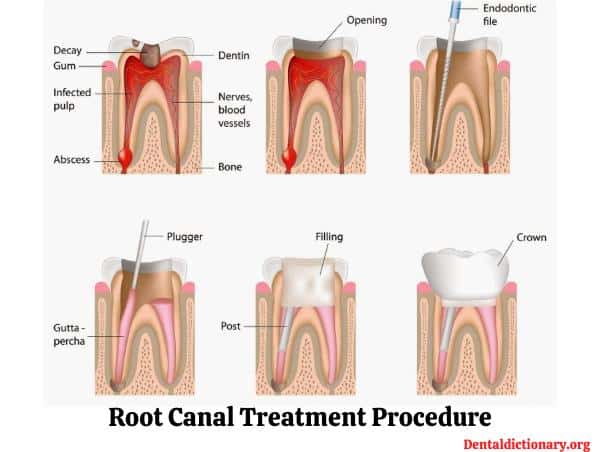
Root canal step by step procedure
Here is the full step by step guide for the root canal treatment procedure.
NOTE: This procedure is only for a quick recap of the dental students or dental graduates. This post is not intended for layman as there are many other reasons that can alter the treatment outcome and this guide is not meant to replace the theoretical knowledge of certified books of this field. Although any one can read this for understanding the concept but he/she shouldn’t use this to treat any problems. A dental visit is must for the treatment.
Local Anesthesia
Local Anesthesia is a very important part of the procedure. It is the first step towards treating the deceased pulp. Since, the patient is having very sharp pain and it needs to subsided before carrying out the root canal treatment procedure.
Thus, Local anesthetic agent is injected to subside that pain and carry out the procedure. It works in 2-3 minutes. The most commonly used local anesthetic for dental procedure is lignocaine (lidocaine).
Dental dam placement (If indicated)
Dental dam placement is an optional procedure. Many dentists use the rubber dam to isolate the tooth before carrying out the procedure while other don’t.
Rubber dam is a latex material used to isolate the tooth on which the treatment procedure is to be carried out.
Access Cavity Preparation
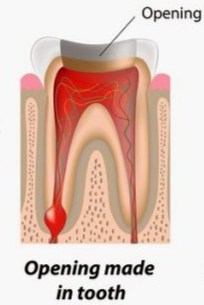
The access cavity is a hole drilled in the tooth for reaching out the pulp. This step also involves removal of all the carious tooth structure.
Goals of Access Cavity preparation
- Removal of all carious tooth structure
- Conservation of sound tooth structure
- Complete deroofing of the pulp chamber
- Removal of coronal pulp tissue (vital and necrotic)
- Location of all root canal orifices
- Straight line access to the root canal
Law of Color Change
- Enamel → White
- Dentin → Yellow
- Floor of the pulp chamber → Gray
- Root canal orifice → Dark gray or black
- Pulp stone → Pearly white/dark yellow
The law of color change in endodontics is necessary for distinguishing between floor of pulp chamber & canal orifices.
Pulp Removal (Cleaning & Shaping)
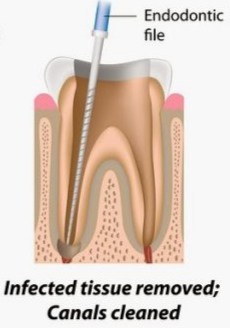
It is the most important part of the root canal treatment procedure as if a small part of the pulp is left in the canal then it can again infect the canal and cause pain to the patient. So, Proper cleaning & shaping is necessary for better outcome.
Goals of Cleaning & Shaping
- To eliminate microorganisms on the canal surface mechanically.
- To completely remove pulp tissue.
- To increase the capacity of the root canal to permit irrigating solutions.
- To shape the canal for insertion of Gutta Percha.
The cleaning and shaping is done by endodontic files of different number for different sizes. Firstly, We have to take the working length, the most common technique for taking working length is ingle’s technique.
Then the root canal instrumentation is done which is done by any of these 3 techniques:
- Step-back technique
- Step-down technique
- Hybrid technique
Irrigation of root canal
Irrigation is necessary for dissolving any left out pulpal tissue in the root canal and also to lubricate the root canal.
Objectives of Irrigation
- Remove the debris created during shaping of the root canal.
- Lubricate the root canal.
- Dissolve organic and inorganic tissues.
- Remove and prevent the formation of smear layer.
The most commonly used irrigant is the sodium hypochlorite(NAOCL) while others are Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and chlorhexidine(CHX).
Obturation of root canal (Root Canal filling)
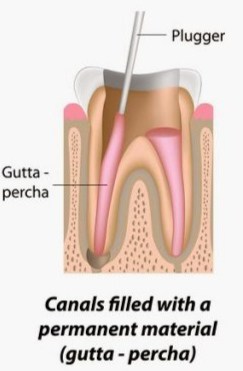
When the tooth is completely cleaned and asymptomatic then the last procedure of root canal treatment is carried on i.e. obturation. In simple words, obturation is the procedure in which a material is filled inside the empty root canal for strength and eliminating all portals of entry between the root canal and periodontium. So, re-infection is also avoided by the help of obturation.
Most commonly used obturating materials are:
- Silver points
- Gutta percha
- Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA)
- Resilon
Most commonly used technique for gutta percha obturation is cold lateral condensation and warm compaction.
Post-obturation (Final Restoration)
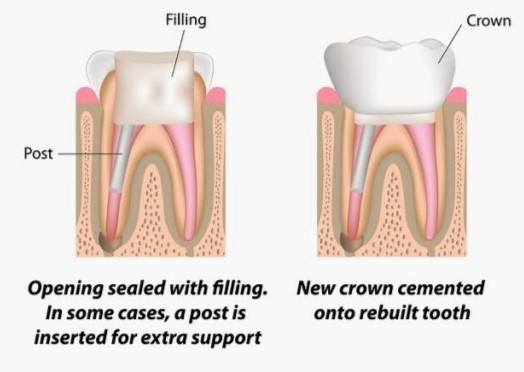
After the gutta percha is filled post obturation is done which is nothing but simple composite material filling on the crown surface for providing strength to the tooth.
After the tooth is filled, the tooth impression is taken for the crown manufacturing procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions regarding Root Canal Procedures
The root canal procedure is time-consuming and can also be frightening for patients who are first time dental clinic visitors. So, here are some of the faqs answered for those patients.
How long does a root canal procedure usually take?
A root canal treatment can be done in 3-4 sittings and also in single sitting if the pulp is not necrosed/critically ill.
In a single sitting root canal procedure, The dentist can take up to 3-3.5 hours.
In a 3-4 sitting procedure, this can be the treatment plan.
DAY 1 – Removal of Carious tissue and Access Opening followed by application of pulp de-vitalizer and cotton.
DAY 2 – Cleaning & Shaping of the tooth followed by temporary restoration and cotton placement.
DAY 3 – Obturation of the root canal and composite filling, if no pain is seen.
Are Root Canal procedure Painful?
The answer is NO! Root canal procedure is done under anesthesia till access opening. Due to this, the area is numbed and no pain is felt.
After that the pulp is removed so the tooth becomes non vital. Pain is not felt in a non-vital tooth.
How long do Root Canal last?
It can last upto 10 years or more if done correctly. 99% of the root canals last about 1 year or more. The root canal can again get infected if proper cleaning and shaping is not done.
Why a crown is placed after Root Canal filling?
After the root canal filling, most of the enamel is removed from the tooth which makes it prone to fractures and also very weak. Due to this, A crown is placed over the tooth after proper crown cutting to preserve the integrity of the tooth.
Alternatives of root canal procedure
Root canal treatment doesn’t have much alternatives, infact the only alternative of root canal treatment is extraction. Other than this if the pulp is exposed without infection or for a short period of time then pulpotomy or direct pulp capping can be done.
REFERENCE: GROSSMAN’S ENDODONTIC PRACTICE 14th EDITION